
Programming Fundamentals
General Course Information
Edirlei Soares de Lima
<edirlei.lima@universidadeeuropeia.pt>
Programming Fundamentals
•
Professor: Edirlei Soares de Lima
–
Education:
•
•
•
B.Sc. in Computer Science – UnC
M.Sc. in Computer Science – UFSM
Ph.D. in Computer Science – PUC-Rio
–
–
Teaching Experience: PUC-Rio, UNIRIO, UERJ, IADE-UE
Game Experience:
•
•
•
Game Engines: RPG Builder, 3D Game Builder;
Research Projects: most are related with Logtell (http://www.icad.puc-rio.br/~logtell/);
Games: Krimson (Best Game Award at SBGames 2010 – Indie Game Development
Festival), and several other prototype games.
–
More Information: https://edirlei.com/
Programming Fundamentals
•
What is computer programming?
–
The process of writing, testing and maintaining a computer program
for accomplishing a specific task.
•
•
What is a computer program?
–
A sequence of instructions that automate the process of performing a
task for solving a specific problem.
How to write a computer program?
–
A computer program is written using a programming language.

Programming Fundamentals
•
•
What is a programming language?
–
A programming language is a vocabulary and set of grammatical rules
for instructing a computer to perform specific tasks.
–
Examples of programming languages: C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript,
HTML, PHP, Python, Lua, Processing, Ruby, Objective-C, Prolog, Go, …
What is the best programming language?
–
There is no "best programming language". It depends on the goals of
the application, platform, programmer’s skills, etc.

Programming Fundamentals
•
•
Games Development:
–
Study the fundamentals of computer programming in a game
development context.
Learning Outcomes:
1
2
3
4
. Understand the concepts of algorithm and program
. Construct algorithms to solve specific problems
. Implement simple graphical and interactive applications
. Apply the concepts learned in the development of small-size
computer games
Programming Fundamentals
•
Module Content:
1
2
3
. Introduction to programming: concepts of algorithm and program
. Introduction to Lua: variables, data types, operators and functions
. Introduction to computer graphics: coordinates, color, transparency,
and Löve 2D
4
5
6
7
8
. Conditional statements and user interaction
. Loops and images
. Vectors, physics and collision detection
. Arrays, matrices, animations and level representations
. Music and audio effects
Method
•
Project-Based Learning:
–
–
–
Learn by doing;
Teamwork;
"Large" project;
•
•
Active and experiential learning:
–
–
–
Theoretical concepts;
Practical examples;
Implementation exercises;
Programming Language: Lua

Evaluation
•
•
Continuous Assessment:
–
–
–
–
–
[20%] Individual exercises on the concepts learned;
[25%] Practical exam on the concepts learned;
[10%] Mini-Project with Math, Physics, and Games I;
[20%] Game prototype (2nd delivery of the semester’s PBL project);
[25%] Final game (final delivery of the semester’s PBL project).
Final Assessment:
–
[100%] Practical exam on the concepts learned.

Evaluation
•
Project deliveries:
–
–
1st delivery: game specification
•
No evaluation for Programming Fundamentals
2nd delivery: working prototype
•
General code organization and indentation, appropriate use of variables,
well-structured loops, appropriate use of arrays, functions and correct
physics simulation
–
3rd delivery: final version
•
Same as the 2nd delivery + overall code complexity and game experience
+ individual discussion + programming report

Lua Programming Language
•
Lua is a powerful, fast, lightweight, embeddable,
free and open-source scripting language designed
for general purposes.
•
•
In video game development, Lua is one of the most
popular scripting language for game programming.
Lua was developed by a team of researchers at
PUC-Rio (Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de
Janeiro) in Brazil.
–
Currently, PUC-Rio has an entire laboratory (LabLua)
dedicated for the development and maintenance of the
Lua language.
Lua Programming Language
•
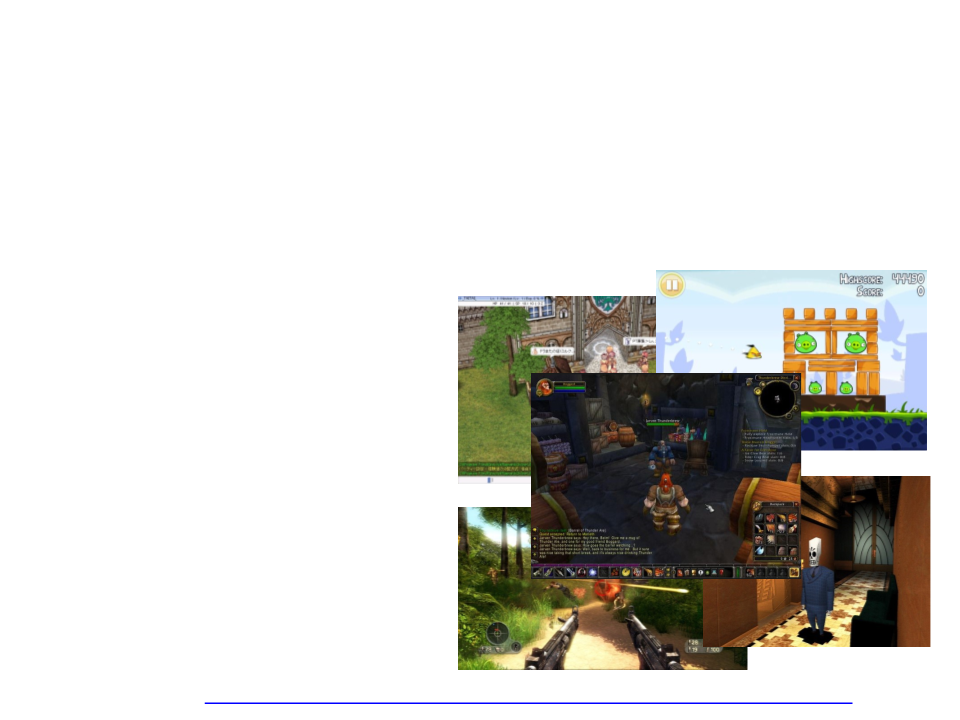
Games that use Lua as scripting language:
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Angry Birds
Civilization V
Far Cry
Grim Fandango
Ragnarok
Dota 2
World of Warcraft

Löve 2D Framework
•
LÖVE is a framework to create 2D games in Lua.
–
It comprises a library of functions to draw visual objects, control user
interaction, simulate physics, play audio, and everything else a game
needs.
–
It's free, open-source and multiplatform (Windows, Linux, Mac OS,
Android, iOS, Web Browsers).
Software
•
•
Löve 2D 11.4: https://love2d.org/
Visual Studio Code: https://code.visualstudio.com/
–
Löve 2D extension:
•
https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=pixelbyte-
studios.pixelbyte-love2d

Example of Game (Lua + Löve2D)
...
function love.draw()
for i = 1, numStars do
love.graphics.setColor(255 - stars[i].speed,
2
1
55 - stars[i].speed/2,
50, stars[i].speed*0.9)
love.graphics.draw(star_image, stars[i].x,
stars[i].y, 0, stars[i].speed/255 + 0.55)
end
love.graphics.setColor(255, 255, 255)
if spaceship_isBoosted == false then
love.graphics.draw(spaceship_image_normal,
spaceship_x, spaceship_y)
else
love.graphics.draw(spaceship_image_boosted,
spaceship_x, spaceship_y)
end
local totalLaserBeams = table.getn(lasers)
for i = 1, totalLaserBeams do
love.graphics.draw(laser_image, lasers[i].x,
lasers[i].y)
end
end
...

Bibliography
•
•
Ierusalimschy, R. (2016). Programming in Lua,
Fourth Edition. Lua.Org. ISBN: 978-8590379867
Ierusalimschy, R., Figueiredo, L. H., Celes, W.
(
Media Limited. ISBN: 978-9888381227
2015). Lua 5.2 Reference Manual. Samurai
•
Christer, E. (2004). Real-Time Collision
Detection. CRC Pres. ISBN: 978-1558607323

Web Resources
•
•
Lua 5.3 Reference Manual: https://www.lua.org/manual/5.3/
Löve Documentation: https://love2d.org/wiki/Main_Page

Programming Fundamentals
•
•
Canvas (Programming Fundamentals):
Course Webpage:
–
https://edirlei.com/gameprogramming
•
Contact:
–
–
edirlei.slima@gmail.com
