
Computer Graphics
Lecture 07 – Shadows
Edirlei Soares de Lima
<edirlei.lima@universidadeeuropeia.pt>
Shadows
•
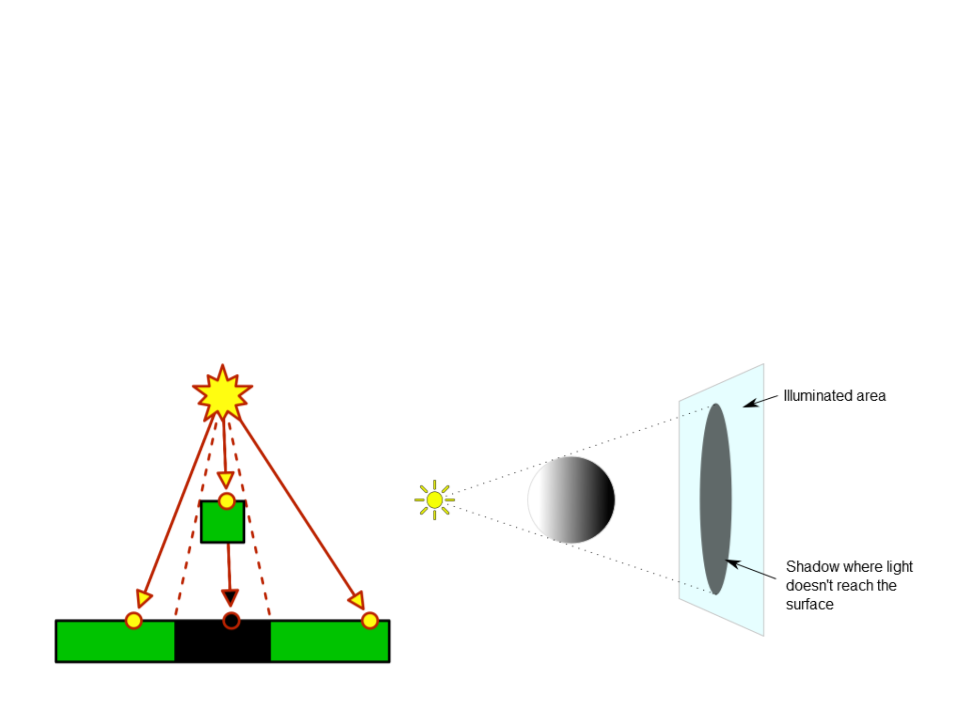
Shadows appear when light rays are blocked: when an object
is between a light source and another object. It prevents the
light rays from reaching the other object.
–
The fist object casts a shadow on the second one.
Shadows in Computer Graphics
•
•
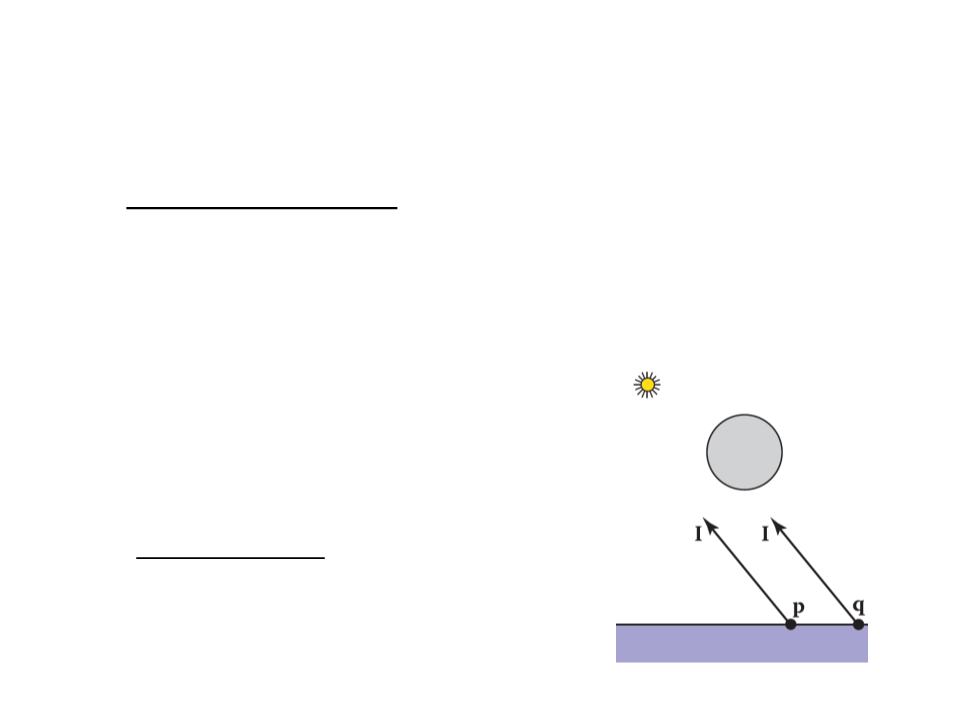
In ray tracing rendering, shadows can be added very easily:
–
Light comes from some direction l;
–
When computing the color of a point p on a surface, the point is in
shadow if we cast a ray in direction l and it hits an object. Otherwise,
the object is not in a shadow.
How to implement shadows in
rasterized renderings?
•
Shadow Mapping!
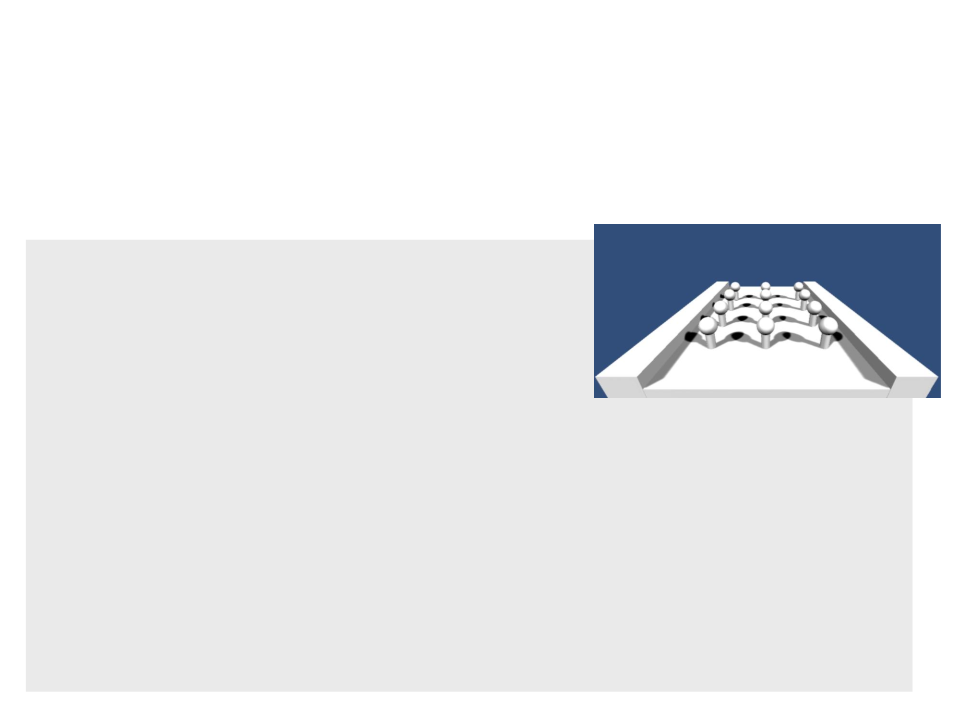
Shadow Mapping
•
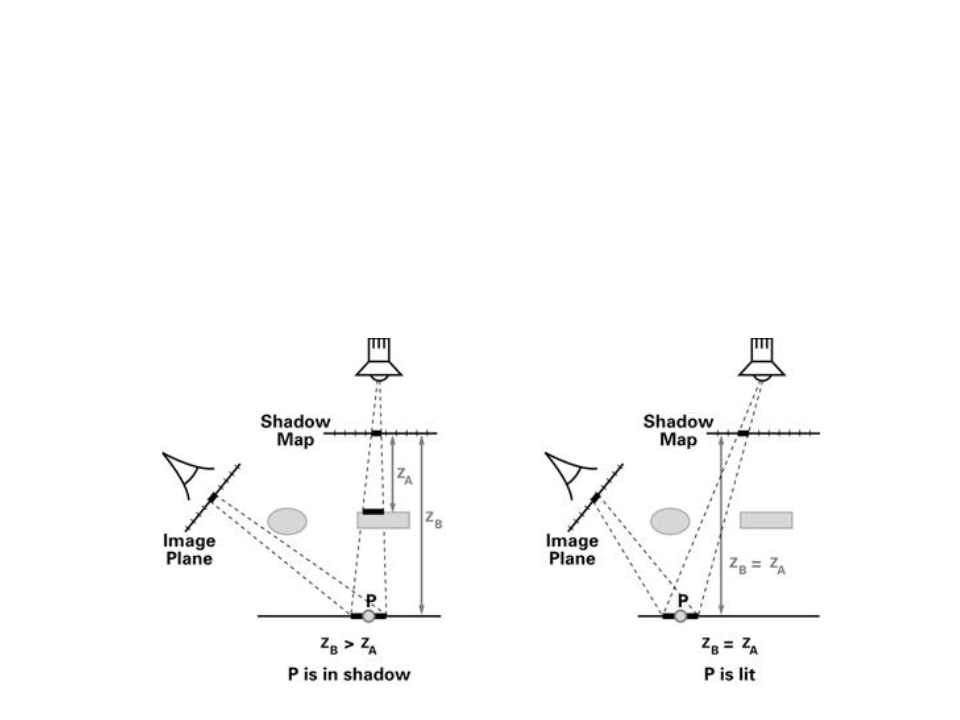
Basic idea: if we looked our scene from the view point of the
light source, all of the objects that we can see would appear
in light. Anything behind those objects, however, would be in
shadow.
Shadow Mapping
•
Algorithm:
–
Step 1: render the scene from the light's point of view (without
calculating light, color or any other shading process).
–
Step 2: extract and save (usually in a texture) the depth buffer from
the rendering (z-buffer generated by the projection process).
•
This texture is called shadow map. If there are multiple lights, a separate
depth map must be used for each light.
–
Step 3: perform a normal rendering pass, and when evaluating
whether a fragment is visible to the light source, project its location in
the shadow map and compare the looked-up value dmap with the
actual distance d to the light source.
•
If the distances are the same, the fragment’s point is illuminated; if the d > dmap,
that implies there is a different surface closer to the source, so it is shadowed.

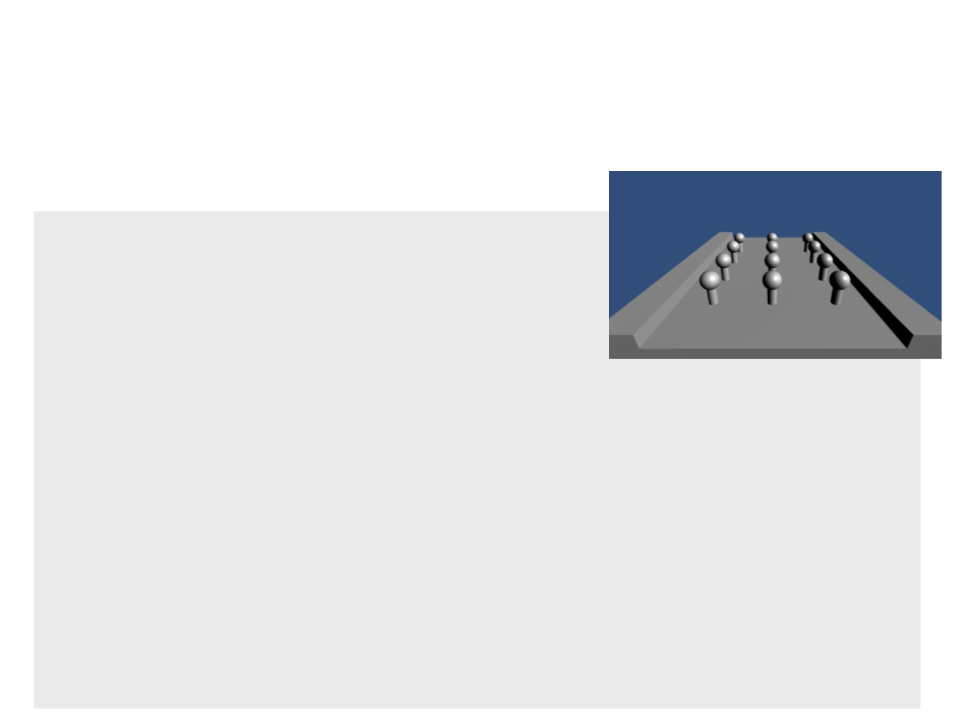
Shadow Mapping Shader
•
In order to implement shadow mapping in a Unity shader, we
need to implement two processes:
–
Cast Shadows: implement a special pass (ShadowCaster) in the shader
to produce the depth data when rendering the scene from the light's
point of view.
•
When Unity detects this pass in a Shader, it automatically renders the object in the
shadow map.
–
Receive Shadows: modify the vertex and fragment programs of the
shader in order to access the shadow map, verify which fragments are
shadowed, and compute their colors appropriately.

Shadow Mapping Shader
•
Cast Shadows:
SubShader{
Pass{
Tags{"LightMode" = "ForwardBase"}
...
}
Pass{
Tags{"LightMode" = "ForwardAdd"}
..
.
}
Pass{
Tags{"LightMode" = "ShadowCaster"}
CGPROGRAM
#
#
#
#
pragma target 3.0
pragma vertex MyShadowVertexProgram
pragma fragment MyShadowFragmentProgram
include "ShadowsShader.cginc"
ENDCG
}
}

Shadow Mapping Shader
•
Cast Shadows:
#
#
if !defined(SHADOWSSHADER_INCLUDED)
define SHADOWSSHADER_INCLUDED
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct VertexData{
float4 position : POSITION;
Using the standard shader on the
ground to visualize the shadows.
};
float4 MyShadowVertexProgram(VertexData vert) : SV_POSITION{
return UnityObjectToClipPos(vert.position);
}
float4 MyShadowFragmentProgram() : SV_TARGET {
return 0;
}
#endif

Shadow Mapping Shader
•
Cast Shadows (bias – light setting to control shadow distance):
#
#
if !defined(SHADOWSSHADER_INCLUDED)
define SHADOWSSHADER_INCLUDED
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct VertexData {
float4 position : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
float4 MyShadowVertexProgram(VertexData vert) : SV_POSITION{
float4 position = UnityClipSpaceShadowCasterPos(vert.position.xyz,
vert.normal);
return UnityApplyLinearShadowBias(position);
}
float4 MyShadowFragmentProgram() : SV_TARGET {
return 0;
}
#endif
Shadow Mapping Shader
•
Receive Shadows:
Pass{
Tags{"LightMode" = "ForwardBase"}
CGPROGRAM
#
#
.
pragma target 3.0
pragma multi_compile _ SHADOWS_SCREEN
..
}
struct VertexToFragment {
...
#
if defined(SHADOWS_SCREEN)
float4 shadowcoords : TEXCOORD2;
endif
#
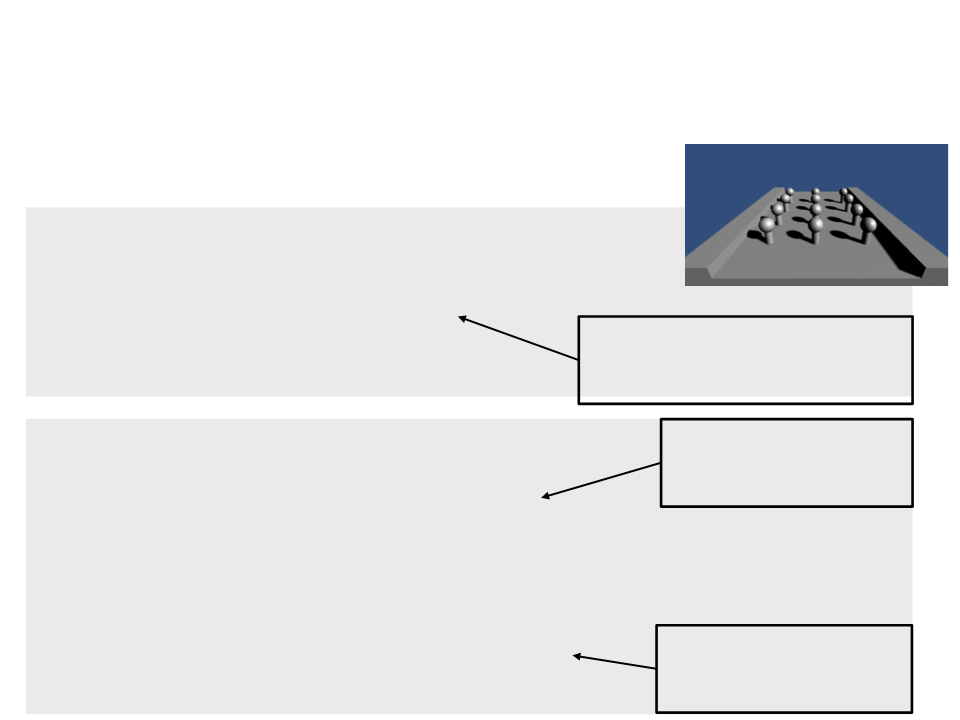
Used to store the screen-space
coordinates of shadow map.
};
Shadow Mapping Shader
•
Receive Shadows:
VertexToFragment MyVertexProgram(VertexData vert){
...
#if defined(SHADOWS_SCREEN)
v2f.shadowcoords = ComputeScreenPos(v2f.position);
endif
#
.
Computes the screen-space
..
coordinates of the shadow map
based on the vertex position.
}
UnityLight CreateLight(VertexToFragment v2f) {
Access the shadow
map values
...
#if defined(SHADOWS_SCREEN)
(
_ShadowMapTexture).
float attenuation = tex2D(_ShadowMapTexture,
v2f.shadowcoords.xy / v2f.shadowcoords.w);
#else
UNITY_LIGHT_ATTENUATION(attenuation, 0, v2f.worldpos);
#endif
light.color = _LightColor0.rgb * attenuation; Multiplies the light
...
color by the attenuation
factor (shadow map).
}
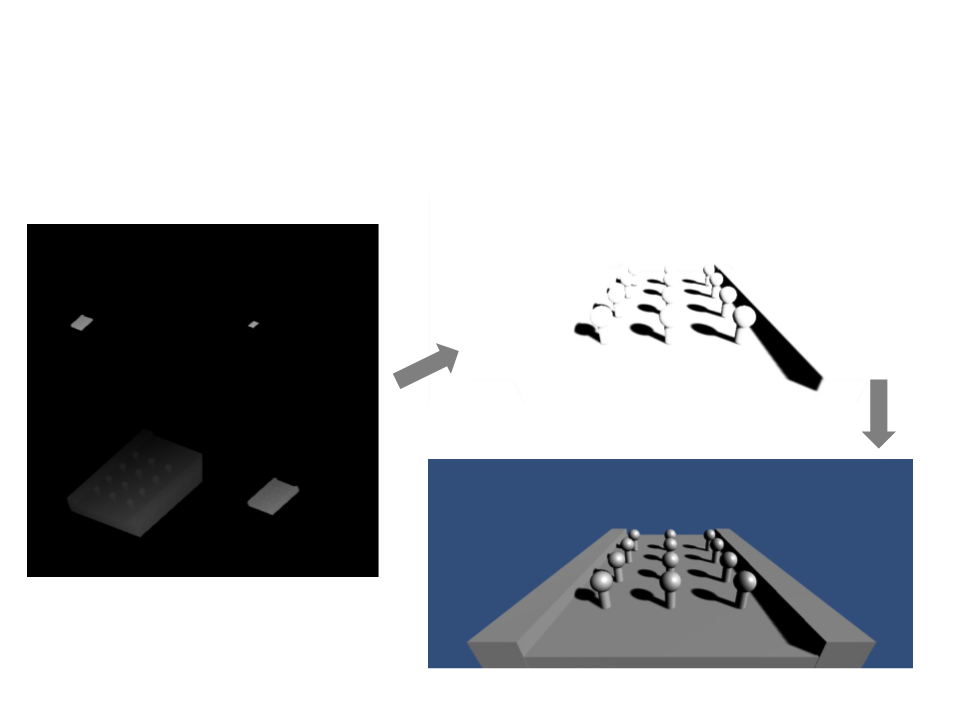
Shadow Mapping Shader
Screen-Space Shadow Map
Shadow Map
Rendered Scene

Shadow Mapping Shader
•
Add support to multiple shadows (directional lights):
Pass{
Tags{"LightMode" = "ForwardBase"}
CGPROGRAM
#
#
.
pragma target 3.0
pragma multi_compile_fwdadd_fullshadows
..
}
Pass{
Tags{"LightMode" = "ForwardAdd"}
Blend One One
ZWrite Off
CGPROGRAM
#
#
.
pragma target 3.0
pragma multi_compile_fwdadd_fullshadows
..
}
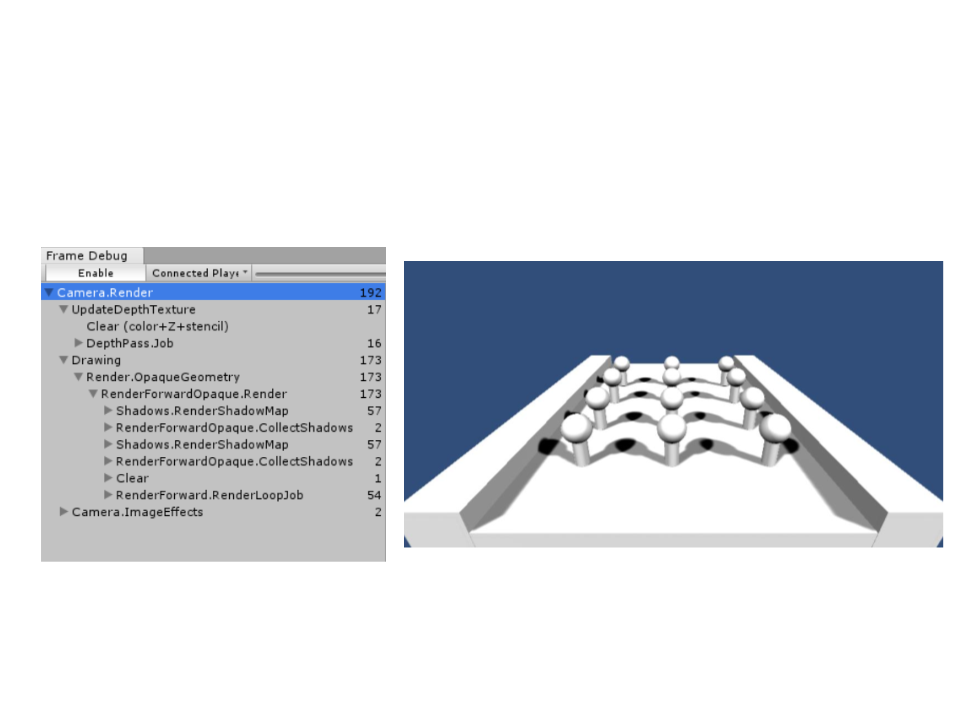
Shadow Mapping – Frame Debbuger

Shadow Mapping – Frame Debbuger
Shadow Map – Light 1
Shadow Map – Light 2
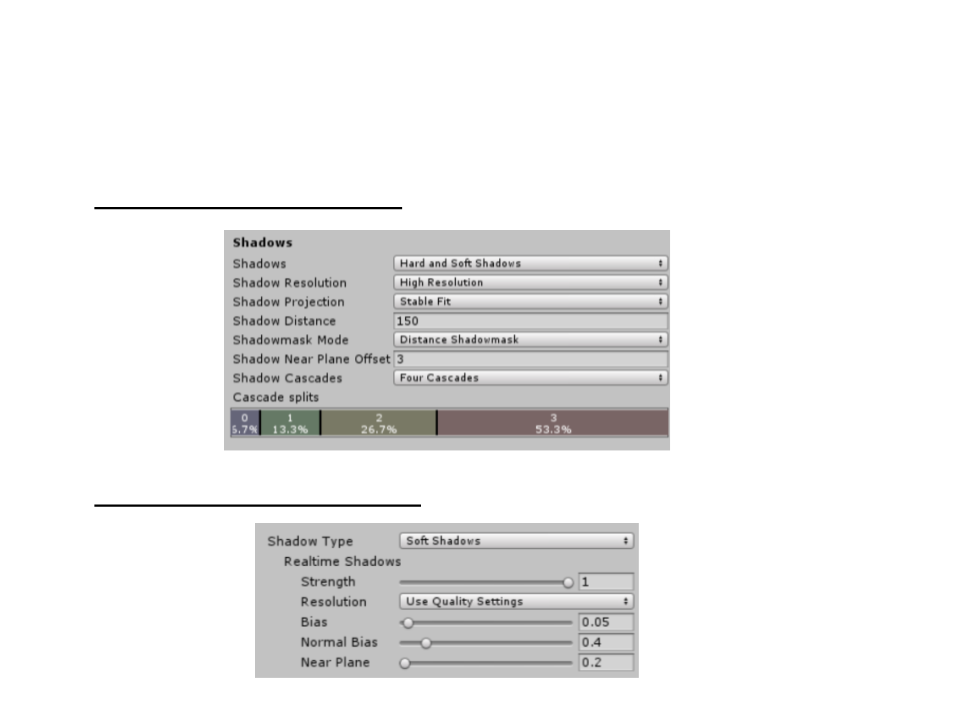
Unity Shadows Settings
•
•
Shadow quality settings: Edit -> Project Settings -> Quality
Shadow settings per light:
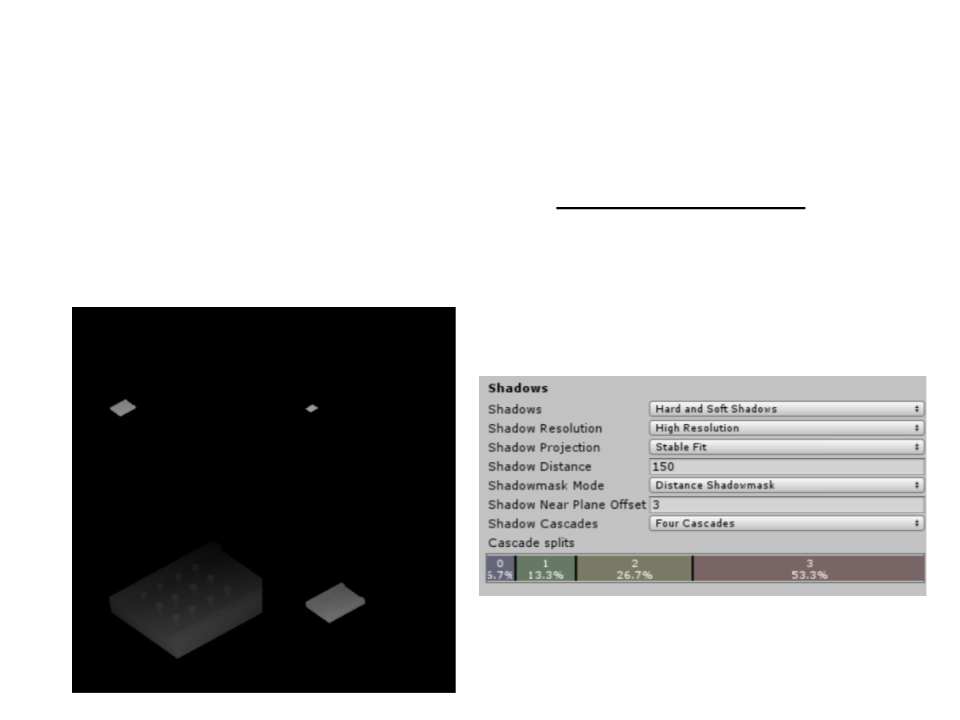
Unity Shadow Maps
•
By default, Unity renders the scene four times per light (cascade
technique). The shadow maps are split into four quadrants,
each being rendered from a different point of view.

Shadow Quality
•
Hard vs. Soft Shadows:
Hard Shadows
Soft Shadows
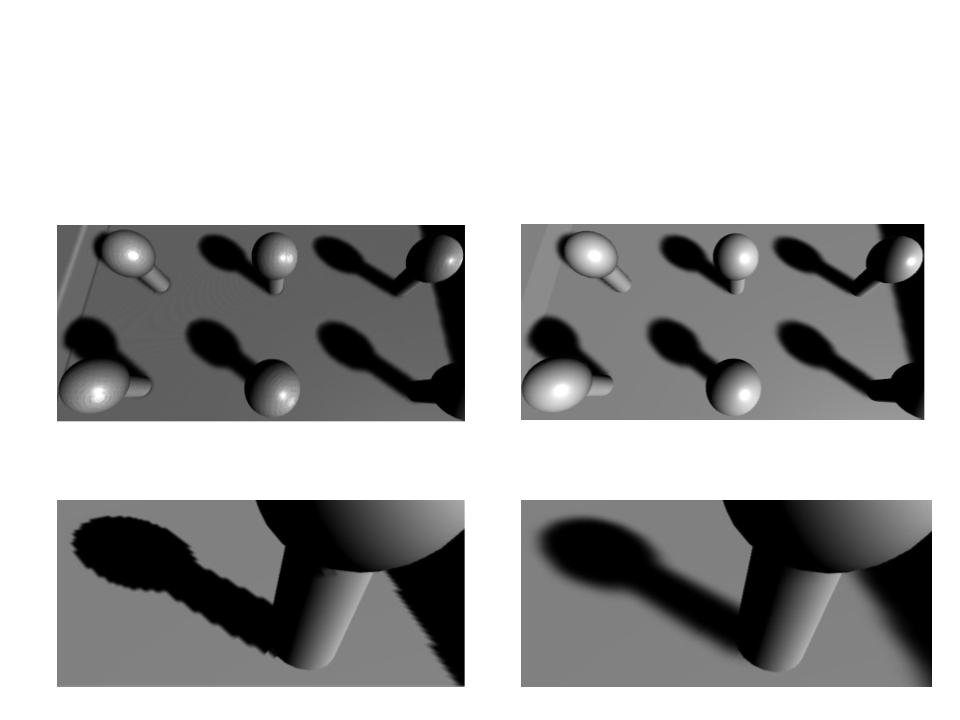
Shadow Quality
Shadow problems:
•
–
Numerical precision limitations (shadow acne):
No bias
With bias
–
Shadow map resolution:
No blur
With Blur
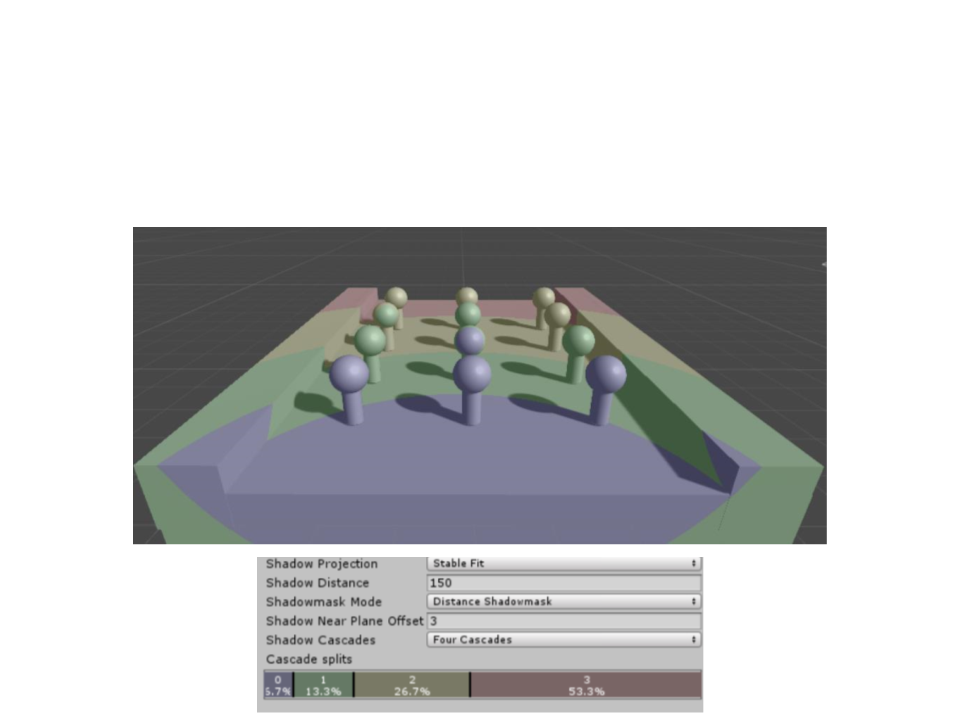
Shadow Quality
•
Cascades Bands:

Further Reading
•
•
•
Hughes, J. F., et al. (2013). Computer Graphics: Principles
and Practice (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Addison-
Wesley Professional. ISBN: 978-0-321-39952-6.
–
Chapter 15: Ray Casting and Rasterization
Marschner, S., et al. (2015). Fundamentals of Computer
Graphics (4th ed.). A K Peters/CRC Press. ISBN: 978-
1482229394.
–
Chapter 11: Texture Mapping
Web:
–
http://catlikecoding.com/unity/tutorials/rendering/part-7/
